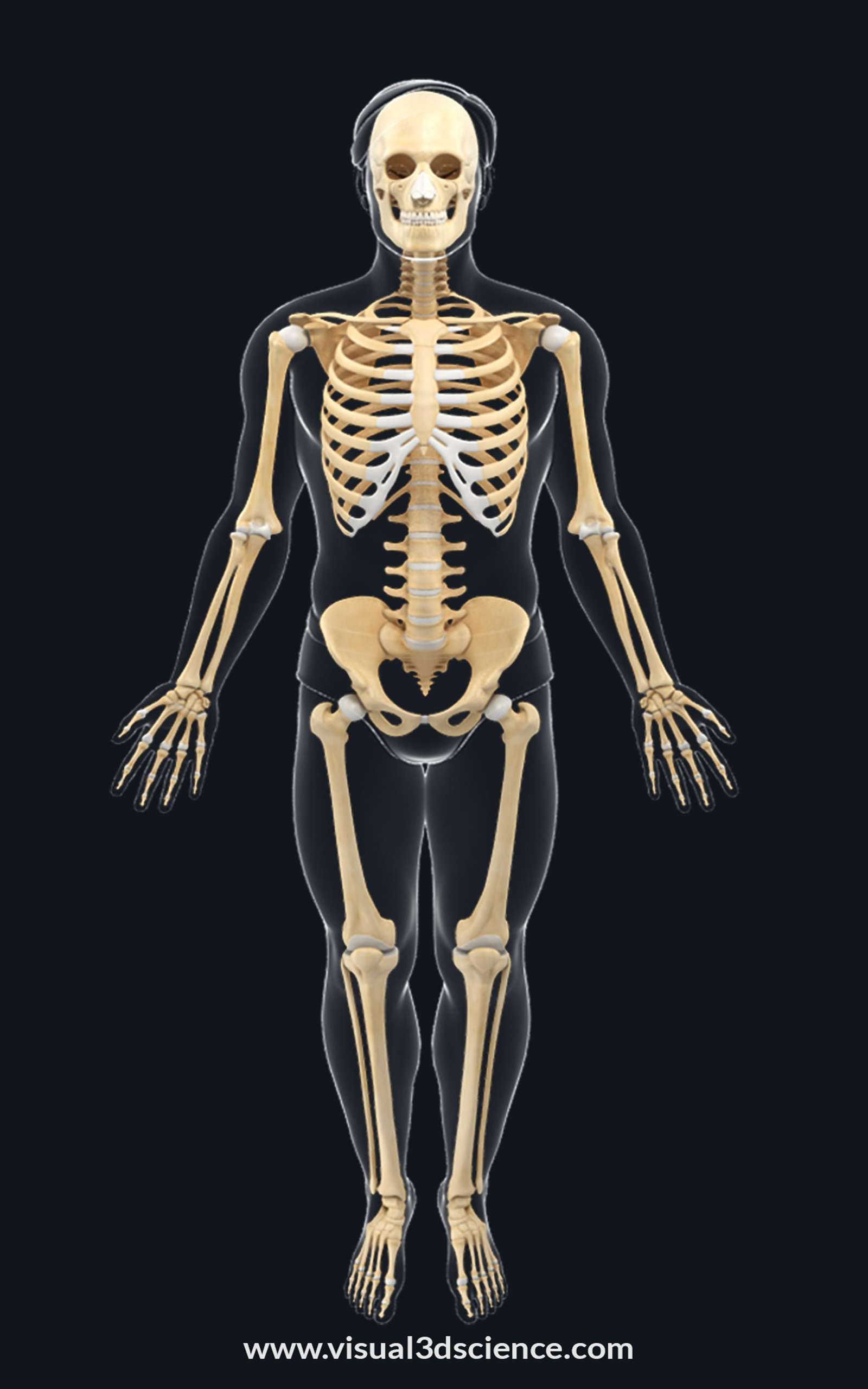
Human bones are hard tissues that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They are used to move, support, and protect the various organs of the body, Inside the bones it where red blood cells are produced.
Here are full details of human bones:
<Structure and Composition>
1. Bone Cells:
- Osteoblasts Cells that form new bone.
- Osteocytes Mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix.
- Osteoclasts: Cells that break down bone tissues.
2. Bone Matrix:
- Composed of collagen (provides flexibility and strength).
- Inorganic minerals (mainly calcium phosphate, which provides hardness)
Types of Bones
1. Long Bones: Found in arms and legs (e.g., femur, humerus respectively).
2. Short Bones: Found in the wrists and ankles (e.g., carpals, tarsals).
3. Flat Bones: Provide protection and covers muscle attachment (e.g., skull, ribs, sternum).
4. Irregular Bones: Have complex shapes (e.g., vertebrae, pelvis).
5. Sesamoid Bones: Embedded within tendons (e.g., patella).
Bone Marrow
- Red Marrow: Produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Yellow Marrow: Stores fat and can convert to red marrow if needed.
Bone Anatomy
1. Diaphysis: The shaft or central part of a long bone.
2. Epiphyses: The ends of the bone, covered with articular cartilage.
3. Metaphysis: The narrow portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis.
4. Periosteum: A dense layer of vascular connective tissue covering the bones.
5. Endosteum: A thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of the bony tissue.
At Champions Health Club we provide consultation services, consultancy and natural solutions that helps our body remail at its optimal health functioning state.